Epidermal growth factor receptor (P00533)
Basic protein information
UniProt Gene
EGFR
Organism
Homo sapiens
Keywords
3D-structure, Alternative splicing, ATP-binding, Cell membrane, Developmental protein, Direct protein sequencing, Disease mutation, Disulfide bond, Endoplasmic reticulum, Endosome, Glycoprotein, Golgi apparatus, Host cell receptor for virus entry, Host-virus interaction, Isopeptide bond, Kinase, Lipoprotein, Membrane, Methylation, Nucleotide-binding, Nucleus, Palmitate, Phosphoprotein, Polymorphism, Proto-oncogene, Receptor, Reference proteome, Repeat, Secreted, Signal, Transferase, Transmembrane, Transmembrane helix, Tyrosine-protein kinase, Ubl conjugation
MemMoRF data
Warning: residue numbering from UniProt, PDB, and papers may differ.
| MemMoRF ID | Region | Supporting statements | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
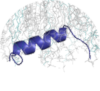
| 9194 | 676-686 |
|
"The JM-A dimer was so constructed that the hydrophobic sides of the amphipathic JM-A helices were in contact with each other. Notably, simulations of this model showed that the JM-A helices were less stable with DMPC lipids than with POPS/POPC lipids." ... "Notably, the JM-A, which was initially placed in solution away from the POPC/POPS membrane, became embedded in the membrane with the JM-A hydrophobic residues buried in the bilayer interior and the basic residues paired with the head groups of the charged lipid." ... "Taken together, these results support a scenario in which the JM-A conformations alternate between the antiparallel JM-A helix dimer and separated JM-A embedded in the membrane, the former corresponding to the active and the latter to the inactive state." (PMID:23374350) "Our results provided evidence for the binding of JX domain peptide to micelles, causing the formation of three helical domains; from residues Lys652 to Arg662, Asn676 to Glu685, and Phe688 to Leu694. All helices were shown to be amphipathic and to use their hydrophobic sides for micelle surface binding (Fig. 7)." ... "...phosphorylation disrupting the helical structure and/or micelles binding of helix 1, causing the recessive basolateral signal (658LL659) to become accessible and thus strengthen the basolateral signal to dominate over the lysosomal sorting signal." (PMID:15840573) "Our NMR analysis shows that the formation of the JM-A helix is coupled to the configuration of the transmembrane helices and occurs outside of the membrane. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest that when EGFR is in an inactive conformation, the LRRLL motif within the JM-A segment is buried in the membrane (Arkhipov et al., 2013), consistent with NMR data for the isolated juxtamembrane segment of EGFR in detergent micelles (Choowongkomon et al., 2005)." (PMID:23374349) "Our data reveal that the chain of EGFR-TMJMA forms two separate helices (TMD and JMA) on residues 646 − 670 and 676 − 686 in DPC micelles." (PMID:26440883) "Our simulations reveal that models of the TM helix and a short 20 residue JM regions of all 58 known human RTKs are able to induce bilayer reorganizations in the form of clustering of PIP2 and PS lipid molecules into shells around the JM region. Selectivity for certain lipid species was evident, with PIP2 found to have the greatest propensity to cluster around the JM regions of all receptors." (PMID:25779975) |
||||||||||
| 9189 | 700-709 |
|
"Our results provided evidence for the binding of JX domain peptide to micelles, causing the formation of three helical domains; from residues Lys652 to Arg662, Asn676 to Glu685, and Phe688 to Leu694. All helices were shown to be amphipathic and to use their hydrophobic sides for micelle surface binding (Fig. 7)." (PMID:15840573) |
||||||||||
| 9190 | 712-718 |
|
"Our results provided evidence for the binding of JX domain peptide to micelles, causing the formation of three helical domains; from residues Lys652 to Arg662, Asn676 to Glu685, and Phe688 to Leu694. All helices were shown to be amphipathic and to use their hydrophobic sides for micelle surface binding (Fig. 7)." ... "The relevance of this structure, in which the JM-A segment is helical, is uncertain because one portion of this peptide is normally integrated into the folded structure of the kinase domain core as a β strand, but instead adopts an α-helical conformation in this micelle-bound peptide." (PMID:15840573) |
Strutures
Genetic
variations/dbSNP
| a.a. change | Type | dbSNP ID | Disesase name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p.Glu709Ala | Polymorphism | within MemMoRF region | 397517085 | - |
| p.Glu709Lys | Polymorphism | within MemMoRF region | 727504256 | - |
| p.Glu709Gly | Polymorphism | within MemMoRF region | 397517085 | - |
| p.Arg98Gln | Polymorphism | 17289589 | - | |
| p.Pro266Arg | Polymorphism | 17336639 | - | |
| p.Gly428Asp | Disease | 606231253 | Inflammatory | |
| p.Arg521Lys | Polymorphism | 2227983 | - | |
| p.Val674Ile | Polymorphism | 17337079 | - | |
| p.Gly719Ser | Polymorphism | 28929495 | - | |
| p.Gly719Ala | Polymorphism | 121913428 | - | |
| p.Gly719Cys | Polymorphism | 28929495 | - | |
| p.Gly719Asp | Polymorphism | 121913428 | - | |
| p.Gly724Ser | Polymorphism | 1051753269 | - | |
| p.Glu734Lys | Polymorphism | 121913420 | - | |
| p.Ser768Ile | Polymorphism | 121913465 | - | |
| p.Val769Met | Polymorphism | 147149347 | - | |
| p.Thr790Met | Polymorphism | 121434569 | - | |
| p.Leu833Val | Polymorphism | 397517126 | - | |
| p.Val834Leu | Polymorphism | 397517127 | - | |
| p.His835Leu | Polymorphism | 397517128 | - | |
| p.Leu838Val | Polymorphism | 864621996 | - | |
| p.Leu858Arg | Polymorphism | 121434568 | - | |
| p.Leu858Met | Polymorphism | 121913443 | - | |
| p.Leu861Gln | Polymorphism | 121913444 | - | |
| p.Arg962Gly | Polymorphism | 17337451 | - | |
| p.His988Pro | Polymorphism | 17290699 | - | |
| p.Leu1034Arg | Polymorphism | 34352568 | - | |
| p.Ala1210Val | Polymorphism | 35918369 | - |
Protein-protein interactions
Click on a node for details.
v. 1.0

 http://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/query/P00533
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/query/P00533
